Math.atan2()
The Math.atan2() static method returns the angle in the plane (in radians) between the positive x-axis and the ray from (0, 0) to the point (x, y), for Math.atan2(y, x).
Try it
Syntax
Math.atan2(y, x)
Parameters
Return value
The angle in radians (between -π and π, inclusive) between the positive x-axis and the ray from (0, 0) to the point (x, y).
Description
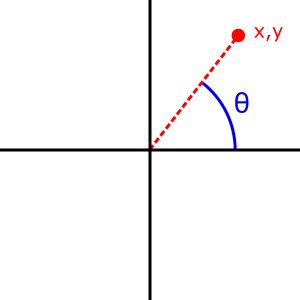
The Math.atan2() method measures the counterclockwise angle θ, in radians, between the positive x-axis and the point (x, y). Note that the arguments to this function pass the y-coordinate first and the x-coordinate second.
Math.atan2() is passed separate x and y arguments, while Math.atan() is passed the ratio of those two arguments. Math.atan2(y, x) differs from Math.atan(y / x) in the following cases:
x |
y |
Math.atan2(y, x) |
Math.atan(y / x) |
|---|---|---|---|
Infinity |
Infinity |
π / 4 | NaN |
Infinity |
-Infinity |
-π / 4 | NaN |
-Infinity |
Infinity |
3π / 4 | NaN |
-Infinity |
-Infinity |
-3π / 4 | NaN |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | NaN |
| 0 | -0 | -0 | NaN |
< 0 (including -0) |
0 | π | 0 |
< 0 (including -0) |
-0 | -π | 0 |
-Infinity |
> 0 | π | -0 |
| -0 | > 0 | π / 2 | -π / 2 |
-Infinity |
< 0 | -π | 0 |
| -0 | < 0 | -π / 2 | π / 2 |
In addition, for points in the second and third quadrants (x < 0), Math.atan2() would output an angle less than
or greater than
.
Because atan2() is a static method of Math, you always use it as Math.atan2(), rather than as a method of a Math object you created (Math is not a constructor).
Examples
Using Math.atan2()
Math.atan2(90, 15); // 1.4056476493802699
Math.atan2(15, 90); // 0.16514867741462683
Difference between Math.atan2(y, x) and Math.atan(y / x)
The following script prints all inputs that produce a difference between Math.atan2(y, x) and Math.atan(y / x).
const formattedNumbers = new Map([
[-Math.PI, "-π"],
[(-3 * Math.PI) / 4, "-3π/4"],
[-Math.PI / 2, "-π/2"],
[-Math.PI / 4, "-π/4"],
[Math.PI / 4, "π/4"],
[Math.PI / 2, "π/2"],
[(3 * Math.PI) / 4, "3π/4"],
[Math.PI, "π"],
[-Infinity, "-∞"],
[Infinity, "∞"],
]);
function format(template, ...args) {
return String.raw(
{ raw: template },
...args.map((num) =>
(Object.is(num, -0)
? "-0"
: formattedNumbers.get(num) ?? String(num)
).padEnd(5),
),
);
}
console.log(`| x | y | atan2 | atan |
|-------|-------|-------|-------|`);
for (const x of [-Infinity, -1, -0, 0, 1, Infinity]) {
for (const y of [-Infinity, -1, -0, 0, 1, Infinity]) {
const atan2 = Math.atan2(y, x);
const atan = Math.atan(y / x);
if (!Object.is(atan2, atan)) {
console.log(format`| ${x} | ${y} | ${atan2} | ${atan} |`);
}
}
}
The output is:
| x | y | atan2 | atan | |-------|-------|-------|-------| | -∞ | -∞ | -3π/4 | NaN | | -∞ | -1 | -π | 0 | | -∞ | -0 | -π | 0 | | -∞ | 0 | π | -0 | | -∞ | 1 | π | -0 | | -∞ | ∞ | 3π/4 | NaN | | -1 | -∞ | -π/2 | π/2 | | -1 | -1 | -3π/4 | π/4 | | -1 | -0 | -π | 0 | | -1 | 0 | π | -0 | | -1 | 1 | 3π/4 | -π/4 | | -1 | ∞ | π/2 | -π/2 | | -0 | -∞ | -π/2 | π/2 | | -0 | -1 | -π/2 | π/2 | | -0 | -0 | -π | NaN | | -0 | 0 | π | NaN | | -0 | 1 | π/2 | -π/2 | | -0 | ∞ | π/2 | -π/2 | | 0 | -0 | -0 | NaN | | 0 | 0 | 0 | NaN | | ∞ | -∞ | -π/4 | NaN | | ∞ | ∞ | π/4 | NaN |
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| ECMAScript Language Specification # sec-math.atan2 |
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser